The world of finance offers various opportunities for individuals to engage in trading, with fixed income trading being one of the most significant areas. Fixed income trading deals with securities that pay a fixed interest over time, such as bonds, Treasury bills, and other debt instruments. These types of investments are favored by investors who prefer steady and predictable returns rather than the high volatility often associated with stocks.
Fixed income traders are financial professionals who specialize in buying and selling these debt securities, providing vital liquidity to the fixed income market. Their role is crucial to the smooth functioning of financial markets, as they help match buyers and sellers while managing interest rate risk and ensuring stable income streams for their clients. In this article, we will delve deeper into the role of fixed income traders, the types of securities they handle, and what it takes to succeed in this demanding profession.
What is a Fixed Income Trader?
 A fixed income trader is a financial professional who specializes in buying and selling fixed income securities, such as bonds, Treasury bills, and other debt instruments. These securities provide regular interest payments and are often considered less risky compared to equities, making them a popular choice for investors seeking stable income. Fixed income traders play a crucial role in managing portfolios, ensuring liquidity in the fixed income market, and helping clients achieve their investment objectives.
A fixed income trader is a financial professional who specializes in buying and selling fixed income securities, such as bonds, Treasury bills, and other debt instruments. These securities provide regular interest payments and are often considered less risky compared to equities, making them a popular choice for investors seeking stable income. Fixed income traders play a crucial role in managing portfolios, ensuring liquidity in the fixed income market, and helping clients achieve their investment objectives.
In this article, we will explore the role of a fixed income trader, the different types of fixed income securities they trade, the skills required to succeed in this profession, and the impact these traders have on the overall financial markets.
Read More: 10 Online Trading Platforms in 2024
Role of a Fixed Income Trader
 A fixed income trader’s primary responsibility is to execute trades involving fixed income securities. These traders work for various institutions, including investment banks, hedge funds, asset management firms, and brokerage houses. Their job involves evaluating market conditions, analyzing financial data, and executing trades in the best interest of their clients or the institution they represent.
A fixed income trader’s primary responsibility is to execute trades involving fixed income securities. These traders work for various institutions, including investment banks, hedge funds, asset management firms, and brokerage houses. Their job involves evaluating market conditions, analyzing financial data, and executing trades in the best interest of their clients or the institution they represent.
The work of a fixed income trader is highly dynamic and requires quick decision-making skills. Traders constantly monitor economic indicators, interest rate changes, and global events that might impact bond prices. Their objective is to profit from price movements in the fixed income market while managing risk effectively. They also work closely with portfolio managers to help design strategies that align with clients’ investment goals, whether those goals involve income generation, capital preservation, or risk mitigation.
Types of Fixed Income Securities
 Types of Fixed Income Securities and Their Characteristics
Types of Fixed Income Securities and Their Characteristics
| Security Type | Issuer | Risk Level | Maturity | Key Features |
| Government Bonds | National Government | Low | Short to Long | Backed by government, low risk |
| Corporate Bonds | Corporations | Medium to High | Short to Long | Higher yield, subject to issuer’s credit risk |
| Municipal Bonds | Local Governments | Low to Medium | Intermediate to Long | Tax advantages, used for public projects |
| Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) | Financial Institutions | Medium | Varies | Backed by mortgage loans, prepayment risk |
| Treasury Bills and Notes | National Government | Low | Short to Medium | Used for short-term liquidity management |
Fixed income traders work with a variety of debt instruments, each of which has unique characteristics and risk profiles. The most common types of fixed income securities include:
- Government Bonds: These are bonds issued by national governments to raise capital. Examples include U.S. Treasury bonds and UK Gilts. Government bonds are typically seen as low-risk investments, given the backing of a sovereign government.
- Corporate Bonds: These bonds are issued by corporations to finance their operations, expansion, or projects. Corporate bonds generally carry a higher risk compared to government bonds, as they are subject to the financial health of the issuing company.
- Municipal Bonds: Municipal bonds, or “munis,” are issued by states, municipalities, or local government entities to fund public projects, such as building schools or infrastructure. These bonds often offer tax advantages to investors.
- Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS): MBS are debt instruments that are secured by a pool of mortgage loans. These securities allow investors to receive interest payments derived from homeowners making mortgage payments.
- Treasury Bills and Notes: Treasury bills (T-bills) are short-term securities that mature in a year or less, whereas Treasury notes (T-notes) have longer maturities. These instruments are commonly used by fixed income traders to manage short-term liquidity.
Key Skills of a Fixed Income Trader
The role of a fixed income trader requires a diverse skill set, combining technical knowledge with the ability to make fast, informed decisions. Here are some of the key skills necessary to succeed as a fixed income trader:
- Analytical Skills: Fixed income traders must have strong analytical skills to assess market conditions and evaluate the value of various fixed income securities. This involves interpreting financial reports, economic data, and interest rate movements.
- Risk Management: Managing risk is an essential part of trading fixed income securities. Traders need to balance potential gains with the risks associated with changes in interest rates, economic conditions, or the creditworthiness of issuers.
- Market Knowledge: Successful fixed income traders possess an in-depth understanding of financial markets and economic principles. They must stay informed about changes in central bank policies, geopolitical events, and other factors that could influence bond prices.
- Mathematical Proficiency: Fixed income trading involves a significant amount of mathematical modeling and calculations. Traders need to understand concepts such as yield, duration, convexity, and credit spreads to make informed decisions.
- Communication Skills: Fixed income traders often work as part of a larger team that includes salespeople, analysts, and portfolio managers. Effective communication is essential to ensure that everyone involved in the investment process is on the same page.
How Fixed Income Traders Make Money
Graph: Relationship Between Interest Rates and Bond Prices
The graph below shows the inverse relationship between interest rates and bond prices. As interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall, and vice versa. This relationship is fundamental to understanding how fixed income traders make money by anticipating interest rate movements and adjusting their trading strategies accordingly.
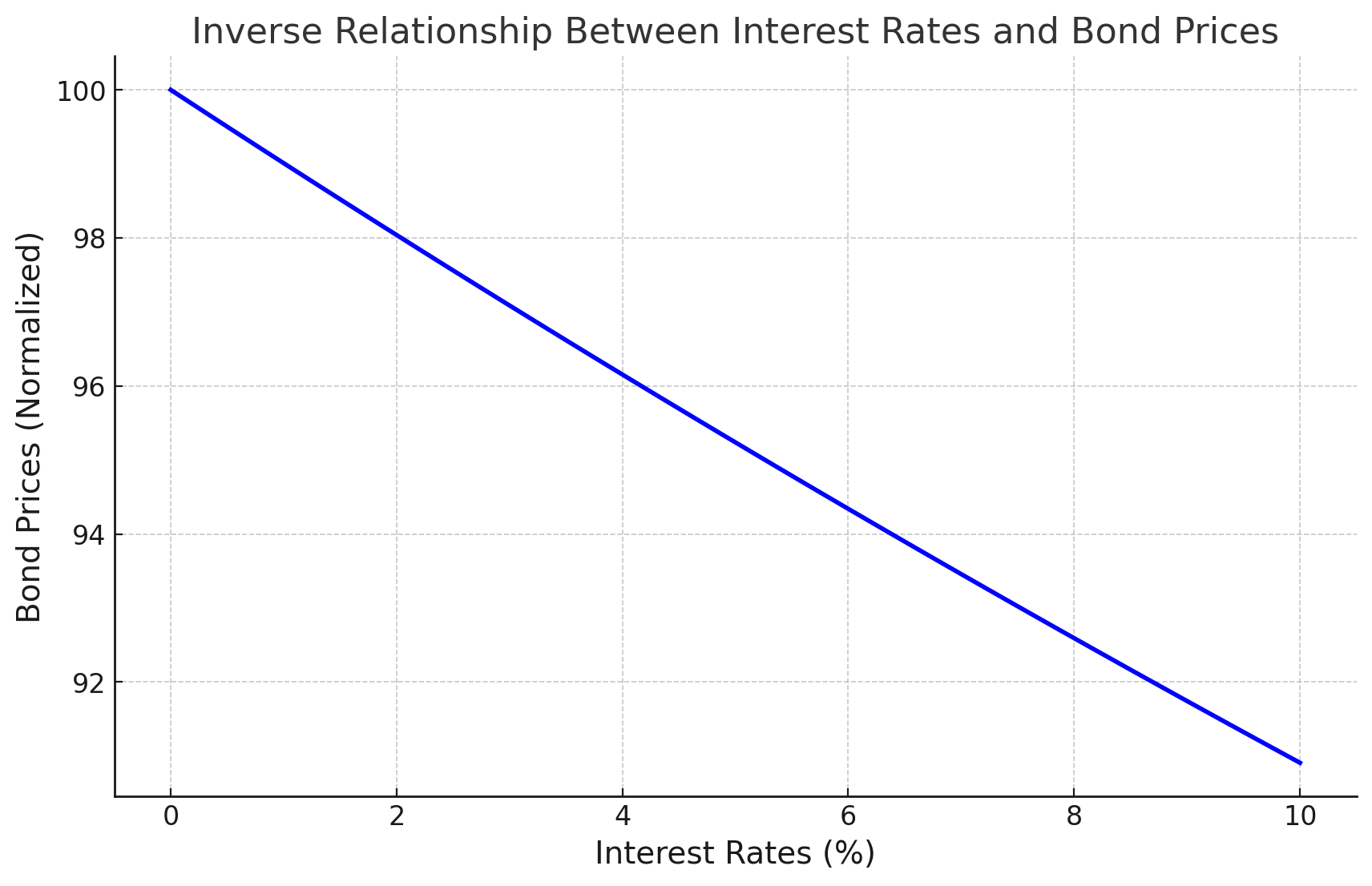 Fixed income traders make money by buying bonds at a lower price and selling them at a higher price, capturing the spread between the two prices. They can also profit by earning commissions on trades they execute for clients. In addition, traders may take advantage of interest rate changes to profit from price movements in bonds.
Fixed income traders make money by buying bonds at a lower price and selling them at a higher price, capturing the spread between the two prices. They can also profit by earning commissions on trades they execute for clients. In addition, traders may take advantage of interest rate changes to profit from price movements in bonds.
Interest rates have a significant impact on the prices of fixed income securities. When interest rates rise, bond prices generally fall, and when interest rates decrease, bond prices typically rise. Fixed income traders leverage their understanding of these relationships to make profitable trades. They use a variety of trading strategies, such as interest rate swaps, curve trades, or spread trades, to capitalize on market movements.
Challenges Faced by Fixed Income Traders
The role of a fixed income trader is not without its challenges. One of the primary challenges is dealing with interest rate risk. Changes in central bank policies or economic conditions can lead to significant interest rate movements, which can impact the value of fixed income securities. Traders must constantly monitor these changes and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Another challenge is managing liquidity risk. Fixed income securities, especially corporate and municipal bonds, can be less liquid than other asset classes, meaning that they might be harder to buy or sell without affecting the market price. This can be particularly challenging during times of market stress or economic uncertainty.
Market volatility is another challenge that fixed income traders must navigate. During periods of high volatility, prices of fixed income securities can fluctuate significantly, creating both opportunities and risks. Traders must be adept at managing these risks while seeking opportunities for profit.
The Importance of Fixed Income Traders in Financial Markets
Fixed income traders play a crucial role in ensuring the liquidity and efficiency of the bond market. By facilitating trades and providing pricing information, they help create a transparent and efficient market that benefits both issuers and investors. Traders help maintain the balance between supply and demand for fixed income securities, ensuring that investors have access to a wide range of options for portfolio diversification.
Additionally, fixed income traders work closely with portfolio managers to develop investment strategies that align with clients’ goals. For example, a portfolio manager may need to adjust a client’s bond portfolio in response to changing interest rates, and fixed income traders execute the necessary trades to implement those changes. Their expertise is essential for achieving desired investment outcomes, whether the focus is on generating income, preserving capital, or managing risk.
How to Become a Fixed Income Trader
Becoming a fixed income trader typically requires a combination of education, training, and experience. Most traders have at least a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, or a related field. Advanced degrees, such as an MBA, can also be beneficial, especially for those looking to advance into senior trading or portfolio management roles.
In addition to formal education, aspiring fixed income traders often complete internships or entry-level positions at financial institutions, where they can gain hands-on experience and learn the intricacies of trading fixed income securities. Professional certifications, such as the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, can also be advantageous for demonstrating expertise and commitment to the field.
Once hired, traders often receive on-the-job training, working under experienced traders to learn the specifics of the fixed income market, the trading platforms used, and the firm’s trading strategies. It takes time to build the necessary skills and develop a deep understanding of the market, but with dedication and experience, traders can advance to more senior positions.
Read More: Best Coding Languages for Trading Algorithms
Conclusion
A fixed income trader plays a vital role in the financial markets, helping to maintain liquidity and efficiency in the bond market while managing risks and seeking profitable opportunities. By trading bonds and other fixed income securities, these professionals contribute to the stability of financial markets and help investors achieve their investment objectives.
The job of a fixed income trader is both challenging and rewarding, requiring a strong understanding of financial markets, analytical skills, and the ability to make quick decisions. For those with a passion for finance and an interest in the bond market, a career as a fixed income trader can be a fulfilling and lucrative path. As the financial markets continue to evolve, the expertise of fixed income traders will remain crucial to ensuring the stability and growth of the fixed income market.

